Electrostatics
Electrostatics is the study of electric charge at rest.Here we study the forces, field, and potentials associated with static charge.
Application of electrostatics
1. In electrostatics loudspeaker.
2. In electrostatics spraying of paints and powder coating.
3. In Flyash collection in chimneys.
4. In a Xerox copying machine.
5. In the design of a cathode-ray tube is used in television and rader.
Electrostatics - frictional electricity
In 600 B.C., Thales, a Greek Philosopher observed that, when a piece of amber is rubbed with fur, it acquires the property of attracting light objects like bits of paper. In the 17th century, William Gilbert discovered that glass, Ebonite etc, also exhibit this property, when rubbed with suitable materials.
The substances which acquire charges on rubbing are said to be 'electrified' or charged. These terms are derived from the Greek word elektron, meaning amber. The electricity produced by friction is called frictional electricity. If the charges in a body do not move, then, the frictional electricity is also known as Static Electricity.
Electric charge
Electric charge is an intrinsic property of elementary particle of matter which gives rise to an electric force between various object.Electric charge is a scalar quantity.It's S.I unit is coulomb(C).
e=1.6 x 10-19 C.
Two kinds of charge
Positive and Negative charge
Benjamin Franklin an American pioneer of electrostatics introduced the present-day conversation by replacing the term vitreous and resinous by positive and negative respectively.According to the convention
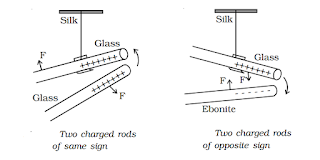
1.The charge developed on a glass rod when rubbed with silk is called Positive charge.
2. The charge developed on a plastic rod when rubbed with wool is called Negative charge.
Electronic theory of frictional electricity
All matter is made of atoms.An atom consists of a small central nucleus containing, protons, and neutrons around which revolved a number of electrons.In any piece of matter, the positive proton charge and the negative electron charge cancel each other and so the matter in bulk is electrically neutral.
The electrons of the outer shelf of an atom are loosely bound to the nucleus.The energy required to remove an electron from the surface of a material is called its "work function".
Conductors
The substance through which electric charges can flow easily is called Conductors.Example:Metal, human are good conductors of electricity.
Insulators
The substance through which electric charges cannot flow easily is called Insulators.Example:Wood, plastic.
Basic Properties of electric charge
Electric charge has following three basic Properties:
1.Additivity
Additivity of electric charge means that the total charge of the system is the system is the algebraic sum of the individual charge located at different points inside the system.
2.Quantisation of electric charge
The fundamental unit of electric charge (e) is the charge carried by the electron and its unit is coulomb. e has the magnitude 1.6 x 10-19 C.
In nature, the electric charge of any system is always an integral multiple of the least amount of charge. It means that the quantity can take only one of the discrete set of values. The charge, q = ne where n is an integer.
3.Conservation of charge
The total charge of the entire universe remains constant.Law of conservation of charge
They can explain in two ways:- The total charge of the isolated system remains constants.
- The electric charges can neither be created nor be destroyed they can only be transferred from one body to another body.